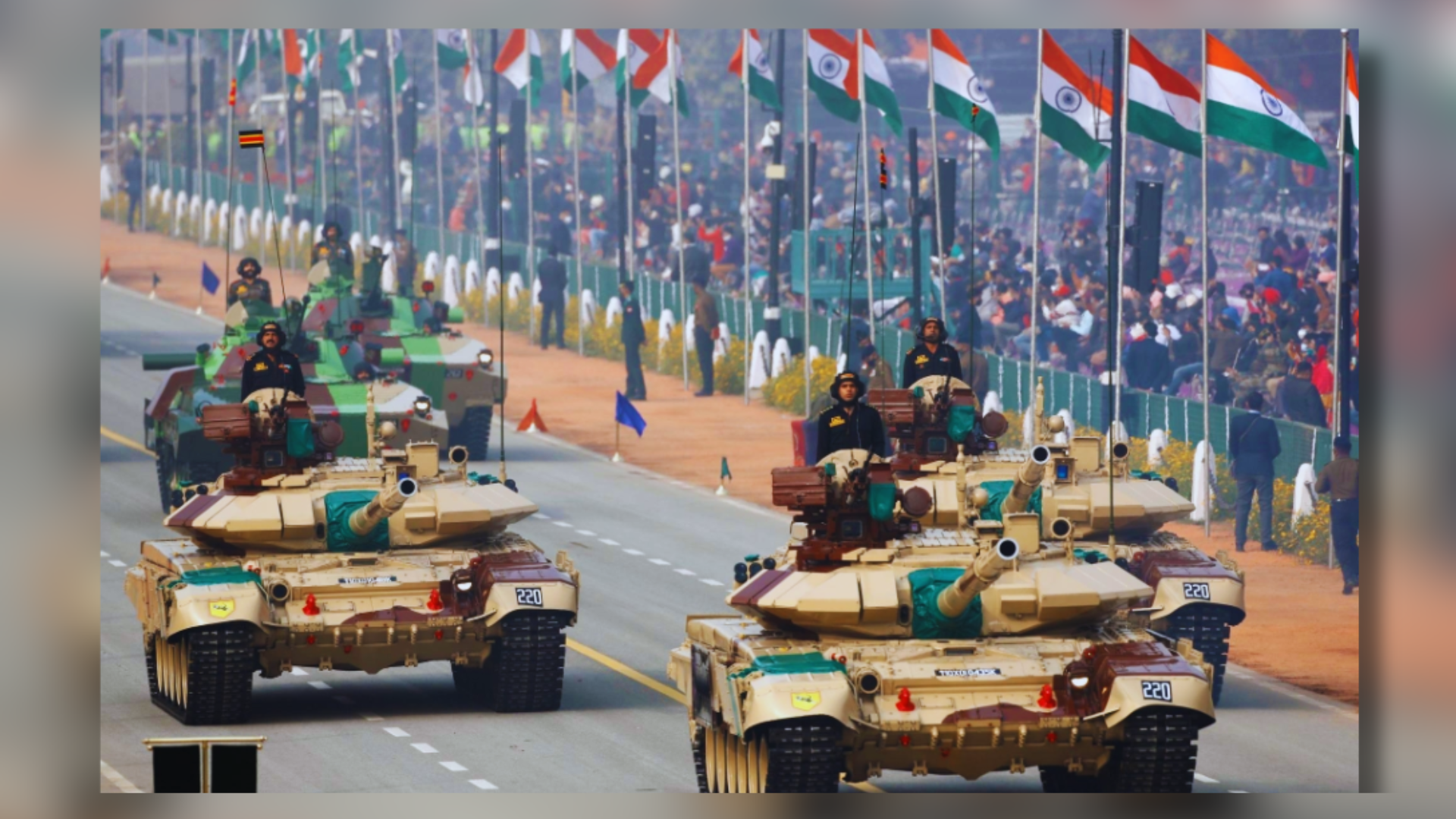
The Indian army is amongst the most powerful armies in the world, standing as the world’s fourth-largest army. The Army has won numerous wars and has come to aid in the most trying situations whether it is disaster relief aid or any high-end rescue operation. The skill of the Indian Army is unparalleled and its biggest strength comes from its diversity that encompasses the image of true India.
Recently, there has been a heavy shift towards a technologically-led world. Consequently, there is a need to revamp a country’s security and defense measures. With this vision in foresight and keeping In light of evolving warfare tactics and geopolitical shifts in the region, the Indian Army (IA) is preparing for a significant modernization endeavor.
During the recent annual Army press conference, Chief of Army Staff (COAS) Manoj Pande announced that 2024 will focus on “technology absorption” for the Indian Army. This shift from the previously declared ‘year of transformation’ in 2023 signifies a significant advancement towards modernization. It can be viewed as a complement to last year’s commitment to transformation, indicating a continuation and enhancement of that pledge.
As the advancement of technology moves further ahead there are numerous new ways in which a threat can be conceived. With the Increase in Drone Operations and the advent of Artificial Intelligence, it becomes imperative for the Nation to opt for a technological transformation.
Steps Taken By The Nation’s Army
The Indian Army (IA) is poised to integrate drones and counter-drone systems across its infantry, artillery, and armored battalions, signaling a proactive approach. Furthermore, the establishment of Command Cyber Operations Support Wings (CCOSWs) underscores a dedication to enhancing cyber capabilities at a structural level.

The army’s adaptability to emerging threats is demonstrated through the reorientation of critical arms like artillery and the infusion of new human resources through Agniveer recruits. Additionally, the army is expanding its human resources pool by cultivating specialist officers through the Territorial Army, including cyber experts through civil-military collaboration. The emphasis on technology as a driver of transformative change is evident in plans to seamlessly integrate drones and counter-drone systems into existing structures.

Communication assumes a critical role with the introduction of 2500 Secure Army Mobile Bharat Version (SAMBHAV) handsets, highlighting the army’s technological self-reliance. The ambitious objective of deploying 35,000 SAMBHAV handsets to personnel managing sensitive tasks emphasizes the dedication to establishing secure and effective communication channels. This holistic approach aligns human resources with the requirements of contemporary warfare, positioning the Indian Army for technological integration in 2024.
What Lies Ahead In 2024
The significance of 2024 for the Indian Army (IA) stems from the profound global changes reshaping the nature of warfare. As nations undergo military modernization driven by larger geopolitical shifts, advanced technologies like lethal autonomous systems, artificial intelligence, hypersonic weapons, directed energy weapons, biotechnology, and quantum technology are becoming pivotal in warfare. For India, China’s expanding capabilities, particularly near Indian borders, pose a significant challenge, especially following the Galwan clashes, where subtle ‘grey zone’ tactics were employed.
In a recent address, the Chief of Army Staff (COAS) highlighted that “Grey zone aggression is increasingly becoming a preferred strategy of conflict prosecution, with its scope enhanced by technological advancements,” indirectly referring to tactics used by both China and Pakistan. Furthermore, the COAS emphasized the necessity for self-sufficiency in critical defense technologies and investment in research and development to counter such aggression.
In addition to the looming threat from China, India is currently grappling with a new form of hybrid militancy originating from Pakistan, which exists inside and along the borders. The rise of ‘hybrid’ militancy in the Kashmir valley, characterized by a blend of conventional and unconventional threats, introduces disruptive elements both along and within the borders.
Solidifying Steady Growth
For the Indian Army, embracing the latest advancements in warfare technology should be viewed as a marathon rather than a sprint. Although the excitement surrounding cutting-edge military technology is undeniable, the process of implementation and adoption unfolds gradually over time.
The Indian Army’s collaboration with academia and industries for innovative solutions through initiatives like Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDex) is commendable. However, there is a need for systematic and long-term initiatives to establish a strong and independent defense industrial base aligned with the army’s requirements.
Specialized training and education are essential for technology proficiency, leading to the introduction of separate cadres for human resources specializing in areas like AI, robotics, and drones. Recently, a new policy allowing Lieutenant Colonels to stay in their technological field upon promotion to Colonel was introduced, deviating from the standard practice of transitioning to command roles.
The Way Forward
The Indian Army’s focus on technology absorption in 2024 brings both promise and scrutiny. While integrating advanced tools like drones and cybersecurity shows a proactive response to evolving challenges, transitioning from a broader transformational agenda requires careful consideration. The urgency prompted by global military trends and the proximity to expanding Chinese capabilities highlights the necessity for swift technological adaptation.
However, potential drawbacks, including the complexities of technology integration and long-term commitment, should not be underestimated. As the army navigates this path, balancing tradition and innovation, a critical eye must remain vigilant, assessing outcomes to ensure that the pursuit of technological prowess aligns seamlessly with national security imperatives.
The success of this strategic shift hinges not just on technology adoption but also on the army’s ability to navigate the complexities and challenges inherent in such a transformative journey.