








The Uttarakhand health department has taken proactive measures to address the rising cases of dengue and chikungunya in the state by issuing comprehensive guidelines aimed at prevention and treatment. These guidelines, comprising twenty crucial points, have been disseminated to District Magistrates and Chief Medical Officers (CMOs) across all districts.
Under the leadership of Secretary Health Dr. R Rajesh Kumar, the department has been conducting regular review meetings to devise effective strategies for preventing the spread of these vector-borne diseases. In consultation with health experts, the department has formulated guidelines focusing on both treatment and prevention measures.
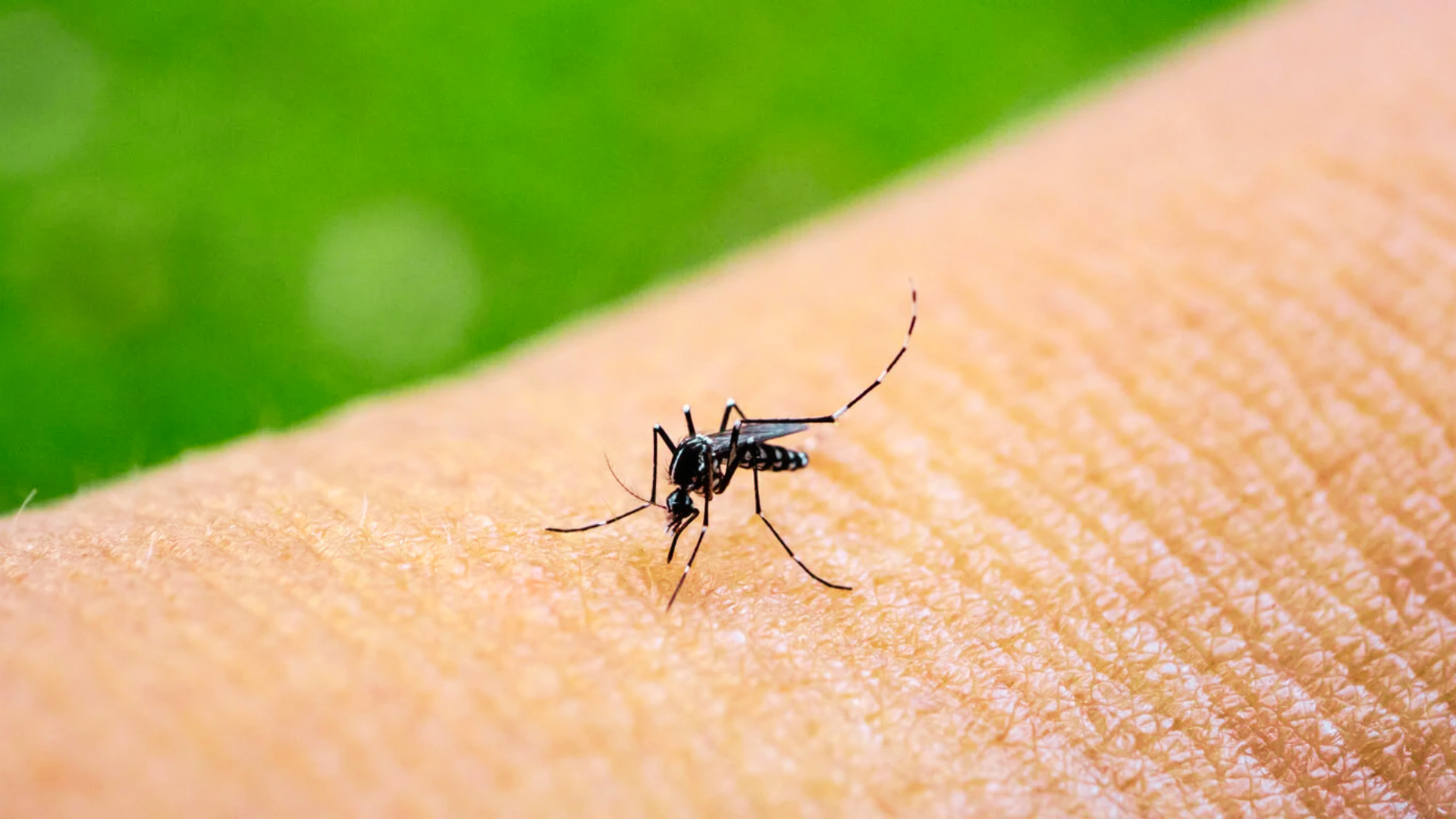
Dr. Kumar highlighted the gravity of the situation, emphasizing that dengue and chikungunya have emerged as significant public health challenges in Uttarakhand in recent years. The Aedes mosquito serves as the vector for these diseases, with the period from July to November being particularly conducive to the spread of the dengue virus. Stagnant water in containers such as coolers, flower vases, pots, open water tanks, old tires, and accumulated debris serves as breeding grounds for these mosquitoes. Dr. Kumar emphasized the critical role of public participation in preventing dengue outbreaks.
ALSO READ: Vice President Dhankhar Praises SILF’s Center As Global Legal Catalyst
Furthermore, Dr. Kumar stressed the importance of coordination among various government departments to effectively combat dengue and chikungunya. He called upon all departments to expedite their efforts in prevention and control measures. Continuous vigilance is necessary to ensure that breeding sites for dengue mosquitoes are promptly identified and eradicated, with district health departments providing ongoing updates on the situation.
To streamline efforts, Dr. Kumar emphasized the need for block-wise micro-planning to be implemented across the state, with action plans submitted to the state NVBDCP (National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme) unit. Municipal corporations were urged to spearhead cleanliness drives to eliminate breeding sites for dengue mosquitoes.
In conclusion, Dr. Kumar reiterated the collective responsibility of all departments in combating the spread of dengue and chikungunya. Timely and concerted action is imperative to safeguard public health and prevent further escalation of these diseases. Through coordinated efforts and community participation, Uttarakhand aims to mitigate the impact of dengue and chikungunya outbreaks and ensure the well-being of its residents.









